Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kimura, Yoshiki; Tsuchiya, Kenichi*
Radioisotopes, 72(2), p.121 - 139, 2023/07
Rapid and precise radioisotope identification in the scene of nuclear detection and nuclear security incidents is one of the challenging issues for the prompt response on the detection alarm or the incidents. A radioisotope identification algorithm using a deep artificial neural network model applicable to handheld gamma-ray detectors has been proposed in the present paper. The proposed algorithm automatically identifies gamma-emitting radioisotopes based on the count contribution ratio (CCR) from each of them estimated by the deep artificial neural network model trained by simulated gamma-ray spectra. The automated radioisotope identification algorithm can support first responders of nuclear detection and nuclear security incidents without sufficient experience and knowledge in radiation measurement. The authors tested the performance of the proposed algorithm using two different types of deep artificial neural network models in application to handheld detectors having high or low energy resolution. The proposed algorithm showed high performance in identifying artificial radioisotopes for actually measured gamma-ray spectra. It was also confirmed that the algorithm is applicable to identifying  U and automated uranium categorization by analyzing estimated CCRs by the deep artificial neural network models. The authors also com-pared the performance of the proposed algorithm with a conventional radioisotope identification method and discussed promising ways to improve the performance of the algorithm using the deep artificial neural network.
U and automated uranium categorization by analyzing estimated CCRs by the deep artificial neural network models. The authors also com-pared the performance of the proposed algorithm with a conventional radioisotope identification method and discussed promising ways to improve the performance of the algorithm using the deep artificial neural network.
Sasaki, Miyuki; Sanada, Yukihisa
Journal of Advanced Simulation in Science and Engineering (Internet), 9(1), p.30 - 39, 2022/01
This study presents the evaluation results of the validity of the visualization map of the ambient dose rate at 1 m above the ground level using an artificial neural network. The dose rate map created using the artificial neural network-based method is found to reproduce ground-based survey results better than conventional methods. Suggested to improve the validity of the airborne radiation survey visualization, applying the color data obtained using a photogrammetry system is a new experience.
Nuclear Human Resource Development Center
JAEA-Review 2021-010, 70 Pages, 2021/09
This annual report summarizes the activities of Nuclear Human Resource Development Center (NuHRDeC) of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) in the fiscal year (FY) 2019.
Onoe, Hironori; Ishibashi, Masayuki*; Ozaki, Yusuke; Iwatsuki, Teruki
International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 144, p.104737_1 - 104737_14, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:34.69(Engineering, Geological)In this study, we investigated the methodology of modeling for fractured granite around the drift at a depth of 500 m in the Mizunami Underground Laboratory, Japan as a case study. As a result, we developed the fracture modeling method to estimate not only geological parameters of fractures but also hydraulic parameters based on the reproducibility of trace length distribution of fractures. By applying this modeling method, it was possible to construct a Discrete Fracture Network (DFN) model that can accurately reproduce the statistical characteristics of fractures.
 at the structure factor primary peak and prepeak
at the structure factor primary peak and prepeakLuo, P.*; Zhai, Y.*; Leao, J. B.*; Kofu, Maiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Faraone, A.*; Zhang, Y.*
Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters (Internet), 12(1), p.392 - 398, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:27(Chemistry, Physical)Using neutron spin-echo spectroscopy, we studied the microscopic structural relaxation of a prototypical network ionic liquid ZnCl at the structure factor primary peak and prepeak. The results show that the relaxation at the primary peak is faster than the prepeak and that the activation energy is
at the structure factor primary peak and prepeak. The results show that the relaxation at the primary peak is faster than the prepeak and that the activation energy is 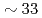 % higher. A stretched exponential relaxation is observed even at temperatures well-above the melting point
% higher. A stretched exponential relaxation is observed even at temperatures well-above the melting point  . Surprisingly, the stretching exponent shows a rapid increase upon cooling, especially at the primary peak, where it changes from a stretched exponential to a simple exponential on approaching the
. Surprisingly, the stretching exponent shows a rapid increase upon cooling, especially at the primary peak, where it changes from a stretched exponential to a simple exponential on approaching the  . These results suggest that the appearance of glassy dynamics typical of the supercooled state even in the equilibrium liquid state of ZnCl
. These results suggest that the appearance of glassy dynamics typical of the supercooled state even in the equilibrium liquid state of ZnCl as well as the difference of activation energy at the two investigated length scales are related to the formation of a network structure on cooling.
as well as the difference of activation energy at the two investigated length scales are related to the formation of a network structure on cooling.
Sasaki, Miyuki; Sanada, Yukihisa; Katengeza, E. W.*; Yamamoto, Akio*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 11, p.1857_1 - 1857_11, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:67.27(Multidisciplinary Sciences)This study proposed a new method to visualize the ambient dose rate distribution using artificial neural networks from the results of airborne radiation monitoring. The method used airborne radiation monitoring conducted around Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant by an unmanned aerial vehicle. A lot of survey data which had obtained in the past was used as training data for building a network. The reliability of the artificial neural network method was evaluated by comparison with the ground-based survey data. The dose rate map that was created by the artificial neural networks method reproduced the ground-based survey results better than traditional methods.
Nuclear Human Resource Development Center
JAEA-Review 2020-008, 74 Pages, 2020/06
This annual report summarizes the activities of Nuclear Human Resource Development Center (NuHRDeC) of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) in the fiscal year (FY) 2018.
Tamai, Hiroshi; Shimizu, Ryo; Tazaki, Makiko; Kimura, Takashi; Nakatani, Takayoshi; Suda, Kazunori
Nihon Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai Dai-40-Kai Nenji Taikai Puroshidhingusushu, p.89 - 92, 2019/11
Libya's denuclearisation, named "the Libya model", is regarded as one of good practices in cooperation of the international community and measures that have a sense of speed with the countries and institutions involved. Success factors of the denuclearisation are the Libya's relatively low technological progress despite the procurement of extensive nuclear materials and components due to the delay of detecting the nuclear programme, prompt implementation with the close collaboration of countries concerned, and Libya's cooperation facing to the economic sanctions and the regime collapse by the Iraq war. Precious lessons will be learned towards the prevention and the denuclearisation in other countries.
Nuclear Human Resource Development Center
JAEA-Review 2019-009, 65 Pages, 2019/09
This annual report summarizes the activities of Nuclear Human Resource Development Center (NuHRDeC) of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) in the fiscal year (FY) 2017.
Sakurai, Satoshi
Genshiryoku No Ima To Ashita, p.287 - 288, 2019/03
no abstracts in English
Kono, Yuko
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 61(2), P. 150, 2019/02
, 61(2), P. 150, 2019/02
no abstracts in English
Nuclear Human Resource Development Center
JAEA-Review 2018-009, 69 Pages, 2018/09
This annual report summarizes the activities of Nuclear Human Resource Development Center (NuHRDeC) of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) in the fiscal year (FY) 2016.
Hayano, Akira; Ishii, Eiichi
Shigen, Sozai Koenshu (Internet), 5(1), 9 Pages, 2018/03
no abstracts in English
Kamikubota, Norihiko*; Yamada, Shuei*; Sato, Kenichiro*; Kikuzawa, Nobuhiro; Yamamoto, Noboru*; Yoshida, Susumu*; Nemoto, Hiroyuki*
Proceedings of 16th International Conference on Accelerator and Large Experimental Physics Control Systems (ICALEPCS 2017) (Internet), p.1470 - 1473, 2018/01
no abstracts in English
Nakajima, Norihiro
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 59(8), p.34 - 38, 2017/08
, 59(8), p.34 - 38, 2017/08
It is necessary the reading comprehension of output data to utilize the simulation in a design process, besides of the input data preparation. The simulation introduces enormous big data for evaluation. This paper describes data analysis technology in the analysis and the evaluation process of the output. The technology applies the artificial intelligence to minimize the unpredictable issues and oversight. It is based on the artifact engineering, which is a multi-sight abduction methodology, which derives a hypothesis.
Saegusa, Hiromitsu; Onoe, Hironori; Ishibashi, Masayuki; Tanaka, Tatsuya*; Abumi, Kensho*; Hashimoto, Shuji*; Bruines, P.*
JAEA-Research 2015-011, 59 Pages, 2015/10
It is important to evaluate groundwater flow characteristics on several spatial scales for assessment of long-term safety on geological disposal of high-level radioactive wastes. An estimation of hydraulic heterogeneity caused by fracture network is significant for evaluation of the groundwater flow characteristics in the region of tens of meters square. Heterogeneity of equivalent hydraulic properties is needed to estimate for evaluation of the groundwater flow characteristics in the region of several km square. In order to develop the methodology for multi-scale hydrogeological modeling taking into account the hydraulic heterogeneity, spatial distribution of fractures and their hydraulic properties have been modeled using discrete fracture network (DFN) model. Then, hydrogeological continuum model taking into account the hydraulic heterogeneity has been estimated based on the DFN model. Through this study, the methodology for multi-scale hydrogeological modeling according to type of investigation data has been proposed.
Sasaki, Akira; Jo, Kazuki*; Kashiwagi, Hiroe*; Watanabe, Chiemi*; Suzuki, Manabu*; Lucas, P.*; Oishi, Masatoshi*; Kato, Daiji*; Kato, Masatoshi*; Kato, Takako*
Journal of Plasma and Fusion Research SERIES, Vol.7, p.348 - 351, 2006/00
no abstracts in English
Akasaka, Hiromi; Takano, Shoji*; Kawamata, Yoichi; Yonekawa, Izuru
Heisei-16-Nendo Osaka Daigaku Sogo Gijutsu Kenkyukai Hokokushu (CD-ROM), 4 Pages, 2005/03
no abstracts in English
Fujita, Mitsutane*; Xu, Y.*; Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Tsukada, Takashi; Mashiko, Shinichi*; Onose, Shoji*
RIST News, (38), p.3 - 14, 2004/11
The distributed materials database system named "Data-Free-Way(DFW)" has been developed with the collaboration of three organizations: the National Institute for Materials Science, the Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute, and the Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute over the Internet since 1990. At present, the development of a distributed knowledge based system, in which knowledge extracted from DFW is expressed, is planned with the collaboration of three organizations as we add data into DFW and make DFW open for the public use. Network technique and presentation and acquisition technique of the information developed rapidly and these techniques brought about a revolution in the society and our daily life changed. This paper describe the present status of DFW and future direction of the material databases with the transition of information technology.
Nakajima, Hidemitsu; Ebisawa, Naomi*; Habara, Tadashi
Dai-1-Kai Joho Purofesshonaru Shimpojiumu (INFOPRO 2004) Happyo Yokoshu, p.103 - 106, 2004/10
no abstracts in English